- Home
- Blog
- Medical Dermatology
- Dupixent: A New Treatment Option for Bullous Pemphigoid, a Rare Skin Disease
Dupixent: A New Treatment Option for Bullous Pemphigoid, a Rare Skin Disease
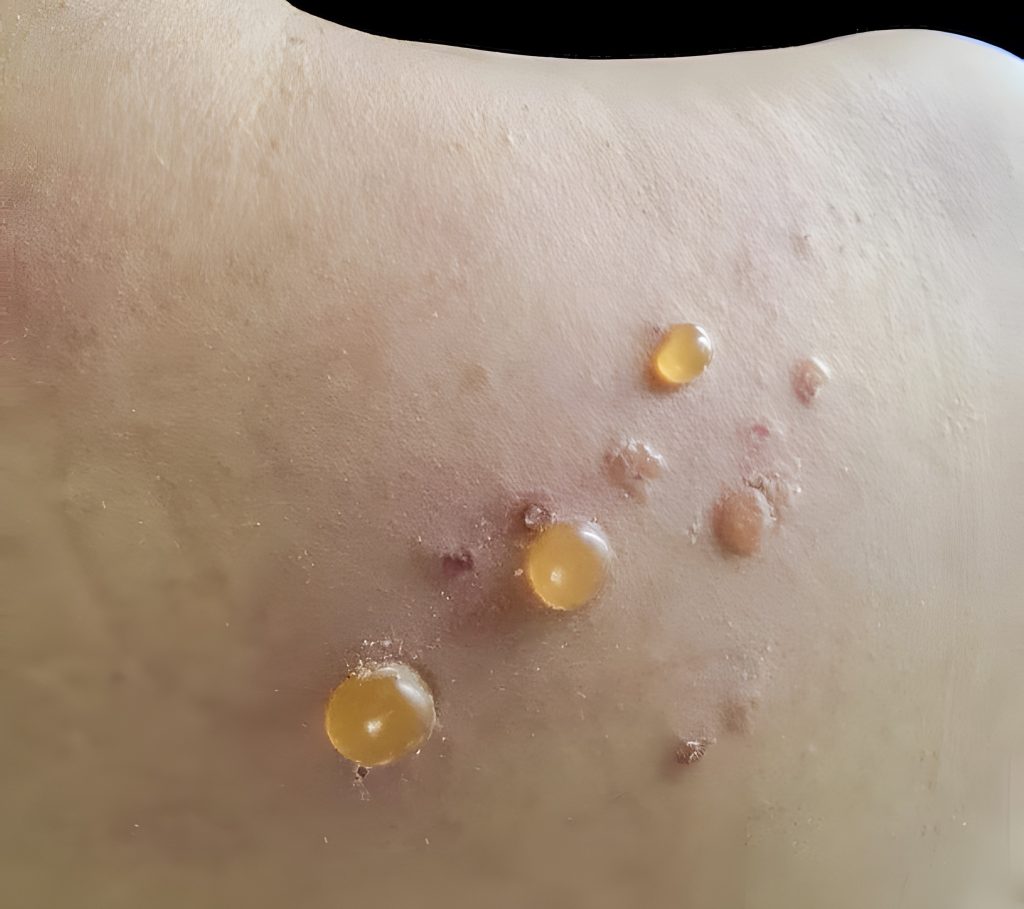 Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare skin disease that mostly affects older adults over 60. It happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks a layer of the skin, leading to painful blisters, redness, and intense itching. While the cause is not fully understood, we now have Dupixent to treat the BP disease.
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a rare skin disease that mostly affects older adults over 60. It happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks a layer of the skin, leading to painful blisters, redness, and intense itching. While the cause is not fully understood, we now have Dupixent to treat the BP disease.
Limitations of current BP treatments
Until now, the main treatment for BP has been high-dose steroids, sometimes combined with other immune-suppressing drugs. While these medicines can help calm the disease, they often cause serious side effects like infections, weight gain, bone loss, and diabetes. Many patients also see their symptoms return once the medicine is reduced.
Dupixent: A targeted approach to BP
In June 2025, the FDA approved Dupixent (dupilumab) as the first targeted treatment for BP. Already established as a cornerstone therapy for atopic dermatitis and recently approved for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), Dupixent takes a more precise approach than traditional immunosuppressants. Instead of broadly shutting down the immune system, the biologic blocks two specific protein signals, called Interleukin 4 (IL-4) and Interleukin (IL-13), that are key drivers of inflammation and blistering in BP.
In a large clinical trial, people taking Dupixent had much better outcomes than those on placebo:
- About 1 in 5 patients reached full disease control, meaning no new blisters and healed skin, while using less or no steroids.
- Nearly 40% had major improvement in their symptoms
- Many reported relief from severe itching.
The most common side effect was mild cold-like symptoms.
A new era of hope for patients
For the first time, people with BP have a treatment designed specifically for their disease. This new approval brings real hope for better control, fewer side effects, and an improved quality of life. If you or a loved one is living with BP, find out what solutions are now possible by consulting with our skilled providers at SkinCare Physicians.



Leave a Reply